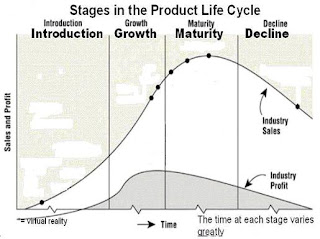
What is Product Life Cycle?
Product life cycle
The course of a product’s sales and profits over its lifetime. It involves live distinct stages product development, introduction, growth, maturity, and decline.
The product life cycle goes through many phases, involves many professional disciplines, and requires many skills, tools and processes. Product life cycle (PLC) has to do with the life of a product in the market with respect to business/commercial costs and sales measures; whereas product life cycle management (PLM) has more to do with managing descriptions and properties of a product through its development and useful life, mainly from a business/engineering point of view. To say that a product has a life cycle is to assert four things:
1) That products have a limited life
2) Product sales pass through distinct stages, each posing different challenges, opportunities, and problems to the seller
3) Profits rise and fall at different stages of product life cycle
4) Products require different marketing, financial, manufacturing, purchasing, and human resource strategies in each life cycle stage.
The different stages in a product life cycle are:
1. Market introduction stage
The product life-cycle stage in which the new product is first distributed and made available for purchase.
- Costs are high
- Slow sales volumes to start
- little or no competition - competitive manufacturers watch for acceptance/segment growth losses
- demand has to be created
- customers have to be prompted to try the product
- makes no money at this stage
2. Growth stage
The product life-cycle stage in which a product’s sales start climbing.
- Costs reduced due to economies of scale
- sales volume increases significantly
- profitability begins to rise
- public awareness increases
- competition begins to increase with a few new players in establishing market
- increased competition leads to price decreases
3. Mature stage
The product life-cycle stage in which sales growth slows or levels off.
- Costs are lowered as a result of production volumes increasing and experience curve effects
- sales volume peaks and market saturation is reached
- increase in competitors entering the market
- prices tend to drop due to the proliferation of competing products
- brand differentiation and feature diversification is emphasized to maintain or increase market share
- Industrial profits go down
4. Saturation and decline stage
The product life-cycle stage in which a product’s sales decline.
- Costs become counter-optimal
- sales volume decline or stabilize
- prices, profitability diminish
- profit becomes more a challenge of production/distribution efficiency than increased sales